What Is Leverage?
Leverage refers to the utilization of borrowing funds to earn higher returns from an investment. Investors can leverage their investments by using a variety of financial products, including options or futures and margin accounts. If investors don't have enough money to buy assets themselves, they take out loans to finance the purchase. The goal is to ensure that the profit on the purchase (ROI) can be higher than the amount borrowed.
Leverage is a way to boost returns; however, it can also increase losses. It is considered a risky investment option that experts should only utilize. For the rest of us, there are less risky methods to reap the benefits of leverage. One of the most effective is a leveraged exchange-traded fund (ETFs).
How Does It Work?
It is believed that the FAS ETF will finance its investments in long-term positions in the particular securities that comprise Russell 1000. It also finances financial instruments that offer the opportunity to leverage and not leverage the Russell 1000 Index, thus creating the potential for returns from the index to triple.
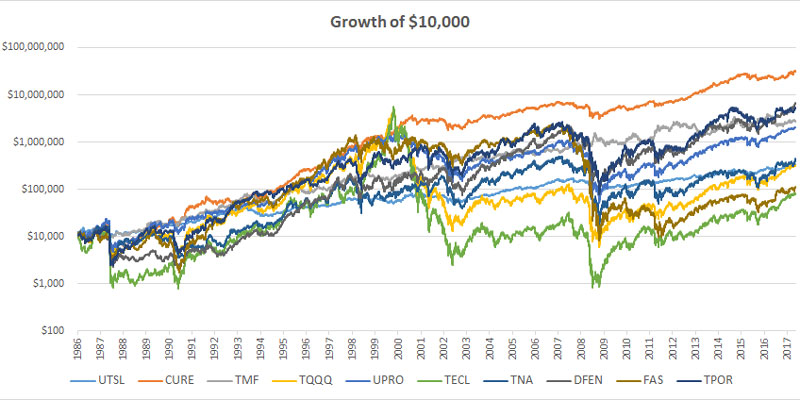
Remember that the fund's five-year return isn't three times the index return. For periods longer than one day, daily rebalancing and the compounding of daily profits will result in the fund's long-term return is different from the index's 300% long-term return. This is because daily profits are compounded over time.
Can I Play the Downside?
The flip aspect of the coin provides investors the chance to profit from the decline in financials with the Direxion Daily Financial Bear 3X Shares ETF (FAZ). This FAZ Fund is designed to provide the reverse of Russell 1000 by creating short positions instead of taking long positions in stocks, as does the Bull friend, the FAS ETF. FAZ's five-year returns FAZ has a five-year return of FAZ is -55.16 percent compared to Russell 1000's 18.75 percent.
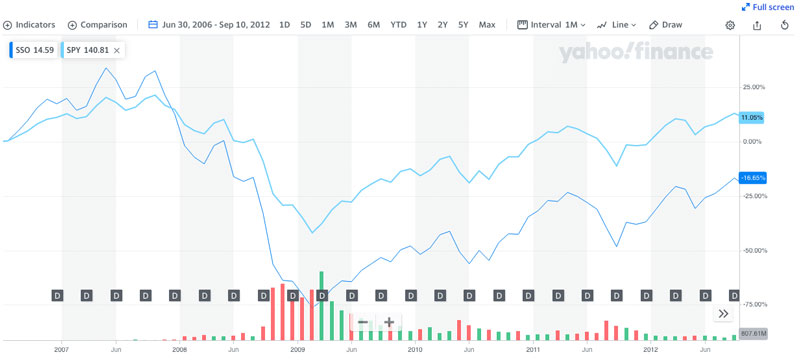
Other 3x Options
ETFs that provide three times the upside (Bull) and three times downward (Bear) can also be found as specific funds. They are those from the Direxion Daily Technology Bull 3X Shares (TECL) as well as the Direxion Daily Technology Bear 3X Shares (TECS). Direxion isn't the only ETF provider that leverages its portfolio, but it is among the most well-known. Additional leveraged ETFs include those provided through ProShares along with MicroSectors.
The Difference between Leveraged and Regular ETFs
A typical ETF is a mutual fund pooled basket containing an underlying set of other assets or securities, usually common stocks. The basket trades under the ticker symbol of its own the day like shares of companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) or Amazon does. At times the net value of assets (the number of securities that are the basis) can differ from the market value. Still, generally, the performance should be in line with the index used to create the long-term performance (minus cost ratio). It's easy enough.
In a leveraged ETF, the fund indeed uses derivatives and loans to increase the returns of the base index at the rate of 2:1 or even 3-to-1 instead of 1-to-1 as the typical ETF. The derivatives and debt employed in these funds pose an excessive amount of risk since they could be able to generate huge gains. Leveraged ETFs are often bundled with higher expense ratios than standard ones.
Who Should Consider Leveraged ETFs?
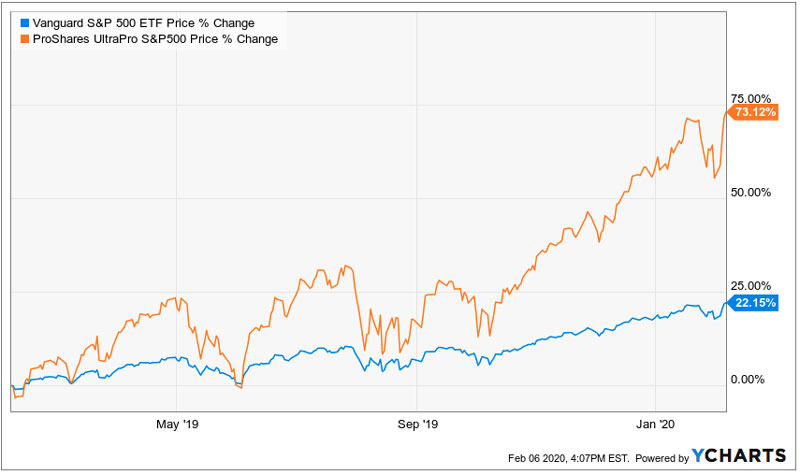
For whom are the leveraged ETFs intended, and why? What individuals or institutions should think about selling or buying these ETFs? It is easy to answer this question once you realize that they're not designed for long-term investments. It is investing in shares in companies, accumulating dividends or lending money, and generating interest income, and is vital for the economic system to function. Investors typically follow long-term strategies and have their goals for the future when purchasing ETFs, stocks, or any other investment.
The idea behind using leverage to increase a benchmark stock market (such as Nasdaq100) by 300 percent and then setting it each day is to bet without the risks of using margin debt. You can choose to take both the long side (bet to bet that the price will grow) and the other part (bet to bet that it'll decline) since both have ticker symbols.