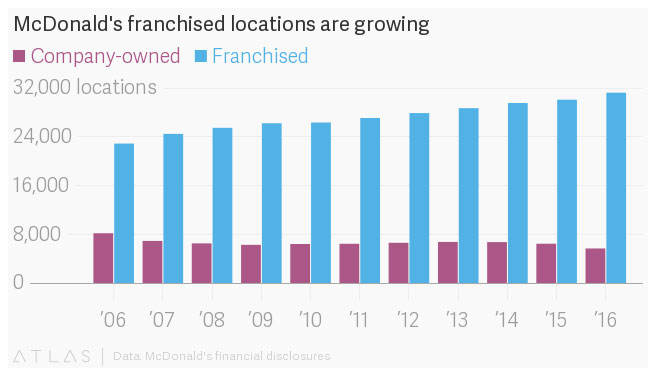
McDonald's generates the majority of its revenue through the licensing of its product, which is fast food, to franchisees who are obligated to lease facilities that are owned by McDonald's at high markups. According to the 2019 10-K report that the firm submitted, 36,059 of the 38,695 stores were franchised, while McDonald's operated the other 2,636 outlets. Therefore, franchisees account for around 93 percent of the overall capacity, which is lower than the long-term aim of 95 percent that McDonald's has set for itself. To get an answer to how McDonald's Makes money, keep on reading.
The income stream is significantly more stable and constant due to using this strategy, which is one of the benefits. In contrast, operational expenses are substantially lower, making the path to profitability significantly less complicated. Because it owns the land and has long-term leases, McDonald's will utilize its market advantage to its advantage to win negotiations.
Why Is McDonald’s Franchisee So Popular?
McDonald's is well-known for having strict standards for prospective franchisees. In addition to this, franchisees are responsible for the payroll of their staff, the ordering of supplies, and the payment of rent or ownership of the property. However, why should you consider purchasing a franchise? The attractiveness lies in that McDonald's gives them an almost certain profit stream, thanks mainly to the enormous margins offered.
The hospitality business is well-known for having a high employee turnover rate. One of the key reasons is that profit margins may be as thin as a piece of processed American cheese, as any restaurant can tell you. This is one of the primary reasons. The answer is that the cost of preparing the meal is far lower than one may first think it to be. Some goods on the menu, like the coffee, fetch prices that are several times more than their production costs.
Growth Strategy

The long-term objective of McDonald's is to franchise around 95 percent of its current restaurant locations. Most of the company's efforts in the future will be focused on re-franchising existing restaurants to traditional licensees to accelerate the achievement of this long-term objective. As the company's business model continues to evolve, various organizational changes to its worldwide business structure have been made to support its efforts to efficiently drive development as a better McDonald's via the Velocity Growth Plan.
The McDonald's Velocity Growth Plan is a customer-centric approach that focuses on the primary drivers of the business, notably food, value, and customer satisfaction. This plan was developed to accelerate the company's expansion. McDonald's is devoted to its three growth accelerators. The following factors are growth boosters:
Experiential Learning for the Future:
The modernization of restaurants and the use of technology advancements are intended to improve the overall customer service experience and the patrons' perceptions of the associated brand.
Digital:
By advancing its digital platform, McDonald's is providing consumers with more options for how they may place orders, make payments, and be served. These new options include expanded features on the company's worldwide mobile app, self-service kiosks, and technologies that enable services like fine dining and curbside pick-up.
Delivery:
McDonald's has increased the number of locations that provide delivery, and the service is now offered in more than half of the chain's restaurants worldwide. When it comes to growing it is brand and company, McDonald's has been and plans to continue to be aggressive in its pursuit of keeping up with the latest developments in the industry. These agreements are an essential component of a plan to stay with younger generations, who would rather have their purchases delivered to their homes than pick them up.
Key Challenges
However, McDonald's may face the most significant threat in the fast-food industry from a customer who wants to eat healthily while still enjoying the convenience of fast food. Since a new restaurant model has been making a concerted effort to get customers' attention, or more accurately, their palates, during the past several years, it has been offering fresher, higher-quality meals in an informal atmosphere and with efficient counter service.
Fast-casual food is different from fast food since it aims to provide customers with healthier options while still providing the convenience of fast food at a higher price. The market share of prominent quick-service restaurants is being eaten away by rising consumer demand for nutritious, affordable, and readily accessible food.
Conclusion
As with any other sector, fast food should have a long-term track record of reliability. People need to eat, yet they don't want to spend much time or money doing so. Nevertheless, the business is confronted with issues arising from changing consumer preferences toward healthier diets. Restaurant chains that emphasize familiarity and regularity must grasp that those attributes are significant advantages. Even if McDonald's has a bad year, the company still makes money.




